Зачем российской промышленности six sigma
Содержание:
- Что такое Sigma
- Section II: Six Sigma
- The 5 Key Principles of Six Sigma
- Как внедрить и использовать концепцию шести сигм
- Why is Lean Six Sigma gaining the importance in today’s scenario?
- Data Evaluation
- What are the Six Sigma Career Choices and Salary Prospects?
- What is Six Sigma?
- Self-Paced Online Training & Certification
- Source Analysis
- Self-Paced Online Training & Certification
Что такое Sigma
Sigma или σ это – греческая буква, которая используется в статистике для обозначения стандартного отклонения.
Объясним, что это такое, на простом примере. Предположим, вам надо быть на работе в 9:00. Каждый день вы добирайтесь до офиса по одному и тому же маршруту и пользуетесь одним и тем же транспортом. Однако на работе вы оказываетесь либо в 8:56, либо в 9:02. И зачастую у вас не получается прийти ровно в 9:00. Другими словами, в процессе есть вариабельность или изменчивость. Более того, изменчивость есть во всем и всегда. Нет ничего абсолютно одинакового: ни людей, ни станков, ни материалов. Все что мы можем – обеспечить минимальное количество отклонений от заданного значения. В таком случае результат будет предсказуемым, а работа управляемой. Чем меньше вариабельность, то есть, чем меньше значение Sigma, тем большее количество продукции или услуг будет удовлетворять требованиям потребителей. А если процесс функционирует на уровне Six Sigma, то 99,9997% продукции будут бездефектны.
Итак, Six Sigma – это концепция управления производством. Ее суть заключается в улучшении качества выходов из каждого процесса, минимизации дефектов и статистических отклонений от заданных параметров в деятельности предприятия. Six Sigma использует статистические методы контроля качества процессов, что требует четкого понимания того, что мы измеряем (какие параметры или переменные) и какие результаты хотим получить.
Для того чтобы использовать концепцию Six Sigma, необходимо отобрать и обучить сотрудников, которые будут не только проводить соответствующие замеры и расчеты, но и обучат своих коллег правильно применять эти методы. Работа в соответствии с этой концепцией предполагает проектное управление и создание команд специально подготовленных сотрудников, которые будут реализовывать проекты по поиску и устранению проблем и улучшению процессов. Обучение и удержание таких сотрудников – дорогостоящее занятие.
Section II: Six Sigma
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a data-driven problem-solving methodology. The focus is on process variations and emphasis is given to customer satisfaction. Continous process improvement with low defects is the goal of this method.
The goal of Six Sigma:
The aim of Six Sigma is to make a process effective with — 99.99996 % defect free. This means a six sigma process produces in 3.4 defects per million opportunities or less as a result.
Six Sigma is a structured problem-solving methodology. Problem-solving in Six Sigma is done using the DMAIC framework. There are five stages in this framework. They are
-
Define,
-
Measure,
-
Analyse,
-
Improve,
-
Control.
Source: Pinterest
|
Six Sigma Phase |
Description of Phase |
|
Define |
In this stage, project objectives are outlined. A project charter is an important component of this phase. A project charter is a blueprint document for a six sigma project. A typical charter contains the following information:
This charter gives an overview of a six sigma project and is approved by top management to give a go-ahead to six sigma project. |
|
Measure |
Process variables are measured at this stage. Process data is collected. The baseline is obtained and metrics are compared with final performance metrics. Process capability is obtained. |
|
Analyse |
Root cause analysis is done at this stage. Complex analysis tools are utilized to identify the root causes of a defect. Tools like histograms, Pareto charts, fishbone diagrams are used to identify the root causes. Hypotheses tests are conducted to verify and validate root causes, Viz Regression test, ANOVA test, Chi-square etc. |
|
Improve |
Once final root causes are identified, solutions need to be formed to improve the process. Steps to identify, test and implement the solutions to eliminate root causes are part of this stage. Simulation studies, Design of experiments, Prototyping are some of the techniques used here to improve and maximize process performance. |
|
Control |
After implementing the solutions, the performance of the solutions must be recorded. A control system must be in place to monitor the performance post improvement. And a response plan is developed to handle solution failure. Process standardization through Control plans & work instructions is typically a part of this phase. Control charts show the process performance. Project benefits are discussed and verified against estimated one. The main purpose of this phase is to ensure holding the gains. |
Table 2: Six Sigma Phases and their descriptions
You may also like: Six Sigma Certification: How does it benefit your career & organization?
The 5 Key Principles of Six Sigma
The concept of Six Sigma has a simple goal – delivering near-perfect goods and services for business transformation for optimal customer satisfaction (CX).
Goals are achieved through a two-pronged approach:

Six Sigma has its foundations in five key principles:
-
This is based on the popular belief that the «customer is the king.» The primary goal is to bring maximum benefit to the customer. For this, a business needs to understand its customers, their needs, and what drives sales or loyalty. This requires establishing the standard of quality as defined by what the customer or market demands.
-
Map the steps in a given process to determine areas of waste. Gather data to discover the specific problem area that is to be addressed or transformed. Have clearly defined goals for data collection, including defining the data to be collected, the reason for the data gathering, insights expected, ensuring the accuracy of measurements, and establishing a standardized data collection system. Ascertain if the data is helping to achieve the goals, whether or not the data needs to be refined, or additional information collected. Identify the problem. Ask questions and find the root cause.
-
Once the problem is identified, make changes to the process to eliminate variation, thus removing defects. Remove the activities in the process that do not add to the customer value. If the value stream doesn’t reveal where the problem lies, tools are used to help discover the outliers and problem areas. Streamline functions to achieve quality control and efficiency. In the end, by taking out the above-mentioned junk, bottlenecks in the process are removed.
-
Involve all stakeholders. Adopt a structured process where your team contributes and collaborates their varied expertise for problem-solving.Six Sigma processes can have a great impact on an organization, so the team has to be proficient in the principles and methodologies used. Hence, specialized training and knowledge are required to reduce the risk of project or re-design failures and ensure that the process performs optimally.
-
The essence of Six Sigma is business transformation and change. When a faulty or inefficient process is removed, it calls for a change in the work practice and employee approach. A robust culture of flexibility and responsiveness to changes in procedures can ensure streamlined project implementation. The people and departments involved should be able to adapt to change with ease, so to facilitate this, processes should be designed for quick and seamless adoption. Ultimately, the company that has an eye fixed on the data examines the bottom line periodically and adjusts its processes where necessary, can gain a competitive edge.
Как внедрить и использовать концепцию шести сигм
Цели концепции шести сигм — улучшить качество продукта или услуги, увеличить удовлетворенность пользователя, сократить потери и сроки проекта. Начать нужно с построения жизненного цикла проекта, чтобы процесс работы был единым для всех.
Жизненный цикл проекта
Для этого используют метод DMAIC: define — measure — analyze — improve — control, или «определяй — измеряй — анализируй — совершенствуй — проверяй». Пять этапов, через которые проходит каждый проект.

Метод DMAIC
Жизненный цикл проекта в системе шести сигм выглядит так.
Шаг №1. Определяй.
- Понять, где вы сейчас и что хотите изменить.
- Улучшить весь процесс или его часть.
- Решить проблемы, которые мешают работе.
- Полностью поменять процессы и подход.
Например, сайт не отвечает требованиям заказчика, разработчики пропускают баги, команда нарушает сроки. Выберем путь решения проблем и попробуем снизить их количество.
Шаг №2. Измеряй. Понять уровень проблем.
За месяц работы и 30 сайтов картина такая: на десяти — нельзя завершить оплату; у пяти — не работает кнопка «Запомнить меня на сайте»; у трех — с главной страницы нельзя перейти в каталог товаров; в двух — нельзя зарегистрироваться, не приходит письмо с подтверждением. Получается20 дефектов:12 критических, три значимых и пять малозначимых.
Классификация багов по степени важности
Вычисляем уровень сигм, то есть отклонений. Для этого делим сумму дефектов на количество сайтов, умноженное на число возможностей возникновения ошибки.
В цикле разработки сайта много процессов. В каждом можно сделать неограниченное количество ошибок. Точного числа нет. Поэтому разделим ошибки на три группы: пожелания заказчика, удобство для пользователя, технические дефекты. И будем считать, что число возможностей совершить ошибку во время разработки одного сайта — три.
Теперь узнаем число дефектов на одну и на миллион возможностей. Для этого умножаем количество запущенных сайтов на число возможностей совершить ошибку, то есть на 3.
30 х 3 = 90
И делим общее количество дефектов на полученное число.
20 ÷90 = 0,2
Получаем 0,02 — число дефектов на единицу или одну возможность. За единицу можно взять один готовый продукт или его часть. Используем один сайт. Чтобы получить число дефектов на миллион возможностей, умножаем результат на миллион.
0,2 х 1000 000 =222 222,2
222 222,2 — число дефектов на миллион возможностей.
Теперь выясним уровень сигм и числа дефектов на миллион возможностей.
Уровень сигм
Число дефектов на миллион возможностей
Процент продукции без дефектов
6
3,4
99,99966%
5
230
99,997%
4
6 210
99,38%
3
66 800
93,32%
2
308 000
69,15%
1
690 000
30,85%
Число222 222,2 находится между66 800 и 308 000, значит, уровень сигм — между2 и 3. Это плохой показатель.
Шаг №3. Анализируй. Проверить показатели.
В нашем процессе много отклонений:20 дефектов на30 готовых сайтов. Что делать? Понять, какие части процесса можно улучшить, как это сделать и с чего начать.
У нас20 дефектов:12 критических, три значимых и пять малозначимых. Сначала боремся с критическими, потом со значимыми. Малозначимые пока откладываем.
Шаг №4. Совершенствуй. Улучшить показатели.
Просто исправить баги недостаточно, нужно научиться их не повторять.
Наши дефекты:
- На десяти сайтах нельзя завершить оплату.
- На двух — нельзя зарегистрироваться, не приходит письмо с подтверждением.
- У трех — на главной странице нет блока с разделами.
Что делать, чтобы не повторять эти ошибки:
- Тестировать после добавления каждой новой функции. В том числе после интеграции с системой оплаты.
- Проверить взаимодействие сайта с разными почтовыми ящиками.
- Писать автотесты для написанного кода.
Мы добавили тестирование после каждого этапа, самые сложные участки работы проверили по несколько раз. Багов стало меньше. Из12 критических осталось пять.
Из значимых — ни одного. Плюс остались пять малозначимых дефектов, которые мы не трогали. Итого: было 20, стало десять.
Шаг №5. Проверяй. Стабилизировать изменения.
На этом этапе нужно еще раз вычислить уровень отклонений, учитывая изменения. Используем уже знакомую формулу и новые показатели.
10 ÷90 = 0,1
Умножаем на миллион, получаем —111 111,1. Снова смотрим в таблицу. Уровень сигм все еще между2 и 3, но процент дефектов уменьшился. Это уже неплохой результат.
Суть этого этапа в том, чтобы сделать стабильными все процессы, которые принесли улучшения. Например, если вы стали тестировать сайт после каждого этапа, а самые сложные участки работы — по несколько раз. Багов стало меньше и вы снова вернулись к привычному процессу работы. То есть не используете полученный опыт и все время возвращаетесь на шаг назад.
Why is Lean Six Sigma gaining the importance in today’s scenario?
Today’s environment is very dynamic. Lean or six sigma approach in this dynamic environment cannot bring full potential to improvements if applied in isolation. Integration of Lean & Six Sigma ensures exceptional improvements. In this management approach, traditionally the lean methodology is used first to remove the waste in a process. Later, the Six Sigma tools are used to improve process variations. However, these two methods go hand in hand in today’s time. The ultimate objective is to improve processes by reducing variation and eliminating waste. It’s a continuous improvement process, where Lean methods and Six Sigma approaches, both take their turn during PDCA. The extent of approaches may differ depending upon process complexities or improvement sought. The combination of these two methods helps to develop streamlined processes with high quality & results. It improves bottom-line profits and helps meeting business goals.
The integrated Lean Six Sigma management approach is being used across sectors and industries. It promotes to exceptional changes in organization’s performance. Lean Six Sigma leads to enjoying competitive advantages in various companies in the world. They can be a product or service-oriented companies. The LSS methodology improves processes and makes them efficient. The key to success is management support, employee engagement and commitment to improving customer satisfaction.
Data Evaluation
At this stage, the collected data is evaluated and sigma is calculated. It gives an approximate number of defects.
-
A Six Sigma defect is defined as anything outside of customer specifications.
-
A Six Sigma opportunity is the total quantity of chances for a defect.
First we calculate Defects Per Million Opportunities (DPMO), and based on that a Sigma is decided from a predefined table −
Number of defects
DPMO = ------------------------------------------- x 1,000,000
Number of Units x Number of opportunities
As stated above, Number of defects is the total number of defects found, Number of Units is the number of units produced, and number of opportunities means the number of ways to generate defects.
For example, the food ordering delivery project team examines 50 deliveries and finds out the following −
- Delivery is not on time (13)
- Ordered food is not according to the order (3)
- Food is not fresh (0)
So now, DPMO will be as follows −
13 + 3
DPMO = ----------- x 1,000,000 = 106,666.7
50 x 3
According to the Yield to Sigma Conversion Table given, below 106,666.7 defects per million opportunities is equivalent to a sigma performance of between 2.7 and 2.8.
This is the method used for measuring results as we proceed through a project. This beginning point enables us to locate the cause and effect of those processes and to seek defect point so that the procedure can be improved.
What are the Six Sigma Career Choices and Salary Prospects?
Six Sigma is a great way to climb up the career ladder with cool job titles and to match salary prospects. Companies that routinely hire candidates to fill Sigma Six positions include 3M, Abbott Laboratories, General Electric, The Hershey Company, IBM, Honeywell, Newell Rubbermaid, Siemens, and Wells Fargo.
There are several career choices for Six Sigma professionals as manufacturing engineers, compliance engineers, and operating system specialists.
Additionally, there are career opportunities with the following titles, although the precise nomenclature can vary from company to company:
- Six Sigma Analyst
- Six Sigma Black Belt
- Six Sigma Consultant
- Director of Operational Excellence
- Functional Project Lead
- Senior Project Manager
- Six Sigma Projects Manager
- Business Process Manager
- Lead Analyst/Project Manager
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a set of management tools and techniques designed to improve business by reducing the likelihood of error. It is a data-driven approach that uses a statistical methodology for eliminating defects.
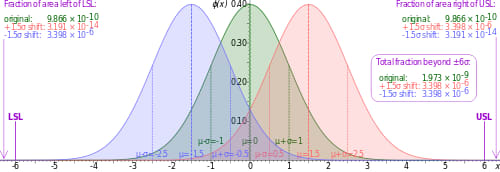
The etymology is based on the Greek symbol «sigma» or «σ,» a statistical term for measuring process deviation from the process mean or target. «Six Sigma» comes from the bell curve used in statistics, where one Sigma symbolizes a single standard deviation from the mean. If the process has six Sigmas, three above and three below the mean, the defect rate is classified as «extremely low.»
The graph of the normal distribution below underscores the statistical assumptions of the Six Sigma model. The higher the standard deviation, the higher is the spread of values encountered. So, processes, where the mean is minimum 6σ away from the closest specification limit, are aimed at Six Sigma.

Self-Paced Online Training & Certification
Want the “Self-Paced” option, but feel like you might need some additional training videos to go with it? Would you like it customized towards your specific industry to boost your qualifications even further?
Aveta Business Institute’s Six Sigma Online is now offering the same flexible option of our “Self-Study” based strictly off of our Body of Knowledge while adding the benefits of training videos, tools, templates, and other supplemental material.
While enrolled in their Black Belt Program, students will still earn their White Belt, Yellow Belt, and Green Belt Certifications while progressing through their Black Belt Program. Their certifications are fully accredited by The Council for Six Sigma Certification and never expire.
In addition, Six Sigma Online offer the largest variety of customized training and certification programs within the Lean Six Sigma industry, such as:
- Lean Six Sigma (Industry Non-Specific)
- Lean Six Sigma in Call Centers
- Lean Six Sigma in Construction
- Lean Six Sigma in Customer Service
- Lean Six Sigma in Distribution
- Lean Six Sigma in eCommerce
- Lean Six Sigma in Engineering
- Lean Six Sigma in Field Services
- Lean Six Sigma in Finance/Banking
- Lean Six Sigma in Food Service
- Lean Six Sigma in Government
- Lean Six Sigma in Healthcare & Medicine
- Lean Six Sigma in Hospitality
- Lean Six Sigma in Human Resources
- Lean Six Sigma in Information Technology
- Lean Six Sigma in Logistics
- Lean Six Sigma in Manufacturing
- Lean Six Sigma in Marketing
- Lean Six Sigma in Military/Defense
- Lean Six Sigma in Retail
- Lean Six Sigma in Sales
- Lean Six Sigma in Supply Chain Management
- Lean Six Sigma in Warehousing
For a full list of industries and descriptions for their Six Sigma Training & Certification Programs, please visit: https://www.sixsigmaonline.org/six-sigma-training/
Source Analysis
This is also called root cause analysis. It attempts to find defects that are derived from the sources of information or work generation. After finding the root cause of the problem, attempts are made to resolve the problem before we expect to eliminate defects from the product.
Three Steps to Root Cause Analysis
-
The open step − During this phase, the project team brainstorms all the possible explanations for current sigma performance.
-
The narrow step − During this phase, the project team narrows the list of possible explanations for current sigma performance.
-
The close step − During this phase, the project team validates the narrowed list of explanations that explain sigma performance.
Self-Paced Online Training & Certification
Want the “Self-Paced” option, but feel like you might need some additional training videos to go with it? Would you like it customized towards your specific industry to boost your qualifications even further?
Aveta Business Institute’s Six Sigma Online is now offering the same flexible option of our “Self-Study” based strictly off of our Body of Knowledge while adding the benefits of training videos, tools, templates, and other supplemental material.
While enrolled in their Black Belt Program, students will still earn their White Belt, Yellow Belt, and Green Belt Certifications while progressing through their Black Belt Program. Their certifications are fully accredited by The Council for Six Sigma Certification and never expire.
In addition, Six Sigma Online offer the largest variety of customized training and certification programs within the Lean Six Sigma industry, such as:
- Lean Six Sigma (Industry Non-Specific)
- Lean Six Sigma in Call Centers
- Lean Six Sigma in Construction
- Lean Six Sigma in Customer Service
- Lean Six Sigma in Distribution
- Lean Six Sigma in eCommerce
- Lean Six Sigma in Engineering
- Lean Six Sigma in Field Services
- Lean Six Sigma in Finance/Banking
- Lean Six Sigma in Food Service
- Lean Six Sigma in Government
- Lean Six Sigma in Healthcare & Medicine
- Lean Six Sigma in Hospitality
- Lean Six Sigma in Human Resources
- Lean Six Sigma in Information Technology
- Lean Six Sigma in Logistics
- Lean Six Sigma in Manufacturing
- Lean Six Sigma in Marketing
- Lean Six Sigma in Military/Defense
- Lean Six Sigma in Retail
- Lean Six Sigma in Sales
- Lean Six Sigma in Supply Chain Management
- Lean Six Sigma in Warehousing
For a full list of industries and descriptions for their Six Sigma Training & Certification Programs, please visit: https://www.sixsigmaonline.org/six-sigma-training/